Pressure measurementis an indispensable monitoring content in the fields of process control, industrial production and manufacturing. Pressure data can help us find problems in time and avoid safety accidents caused by abnormal pressure. In pressure measurement, positive pressure and negative pressure are relative concepts. In this article, we will introduce the concepts and difference between positive pressure and negative pressure to you so that you can better understand pressure.
Positive Pressure Definition
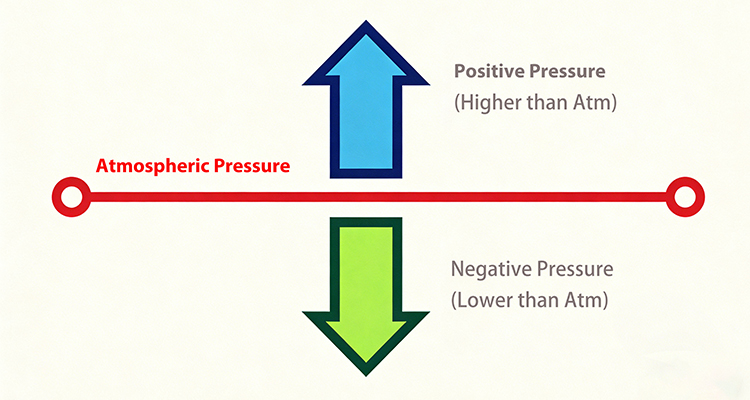
Positive pressure refers to the pressure value of atmospheric pressure at that time, and also refers to the positive gauge pressure value. The formula is: P positive pressure = P ab-P atm. Positive pressure measurement is used in oil, natural gas and chemical pipelines, chemical reaction vessels and other closed equipment, energy and power systems, ventilator equipment and other medical pressure monitoring.
Negative Pressure Definition
Negative pressurerefers to the pressure value lower than atmospheric pressure, which can also be called vacuum pressure. The formula is: Pnegative pressure = Patm-Pab. Negative pressure can be effectively used in the medical industry, such as chest drainage, negative pressure wound treatment, industrial and manufacturing industries such as vacuum packaging, vacuum distillation, vacuum coating, etc., construction and environmental engineering, energy and power systems, etc.
Positive Vs Negative pressure
Positive pressure and negative pressure are values relative to atmospheric pressure, where the pressure value of atmospheric pressure is called positive pressure, and the value below atmospheric pressure is called negative pressure. Atmospheric pressure values vary due to regional differences. Therefore, the positive and negative pressure values under standard atmospheric pressure may have different pressure values in different places. The fluid in a positive pressure state flows from the inside of the system to the outside, while the fluid in a negative pressure state flows from the outside to the inside. In short, in practical applications, we should choose the appropriate pressure type according to our applications.
Aspect
|
Positive Pressure
|
Negative Pressure (Vacuum)
|
Basic Definition
|
Pressure state above the local ambient atmospheric pressure.
|
Pressure state below the local ambient atmospheric pressure, commonly referred to as a "vacuum."
|
Fluid/Gas Direction
|
Fluid/gas flows from inside the system to the outside.
|
Fluid/gas flows from outside the system to the inside.
|
Typical Applications
|
- Industry: Hydraulic systems, pneumatic tools, pipeline transport, pressure vessel testing.
- Medical: Ventilators (e.g., CPAP), ventilation in sterile rooms.
- Daily Life: Inflating tires, spray cans.
|
- Industry: Vacuum suction cups, vacuum packaging, vacuum distillation, semiconductor manufacturing.
- Medical: Negative pressure isolation rooms, operating theaters, wound suction devices.
- Daily Life: Vacuum cleaners, drinking through a straw.
|
Common Measurement Devices
|
Pressure gauge, gauge pressure sensor.
|
Vacuum gauge, vacuum sensor, compound pressure sensor (negative range).
|
Conclusion
Pressure measurement is an essential process in process control, petrochemical, constant pressure water supply, machinery manufacturing and other fields. It can make our work safer, more stable and more reliable. Positive pressure and negative pressure are two different types of pressure measurement. Understanding their concepts and differences will help us betterchoose the right pressure product.
FAQ
Q:What is the fundamental difference between positive and negative pressure?
A: The most fundamental difference lies in their reference to local atmospheric pressure. Simply put, positive pressure refers to a state where pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure, while negative pressure refers to a state where pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure (also referred to as a vacuum).
Q: Can you give examples of positive and negative pressure applications in the medical field?
A: Certainly. In medicine, positive pressure is commonly used in ventilators to push oxygenated air into a patient's lungs. Negative pressure is used in ventilation systems for operating rooms or isolation wards to ensure air flows only from outside into the room, preventing contaminants from spreading outward. It is also used in wound suction therapy.
Q: What are some industrial scenarios that utilize negative pressure (vacuum)?
A: Industrial applications of negative pressure are extensive, including vacuum packaging (removing air from bags to extend food shelf life), vacuum suction cups (for material handling), vacuum furnaces (for precision heat treatment or coating), and vacuum distillation in chemical processes.
Q: How does a positive pressure system ensure safety?
A: In chemical or energy industries, maintaining pipelines or reaction vessels under positive pressure prevents external air or contaminants from leaking into the system. This avoids pollution, explosions, or unwanted chemical reactions, serving as a crucial safety control measure.
Q: Can the same sensor be used to measure both positive and negative pressure?
A: It depends on the sensor type. Compound pressure sensors can measure both positive and negative pressure. However, for measuring unidirectional pressure, one typically needs to select either a dedicated gauge pressure sensor (for positive pressure) or a vacuum pressure sensor (for negative pressure).
Q: How does a "negative pressure isolation room" work?
A: A negative pressure room uses a ventilation system to actively exhaust air from inside, maintaining a room pressure consistently lower than the pressure outside. This ensures that when a door or window is opened, only clean external air flows in, while potentially contaminated air inside is filtered before being exhausted, effectively preventing the spread of viruses or bacteria to the outside.
Q: Can we experience positive or negative pressure in a home environment?
A: Yes. For example, when you use a vacuum cleaner, its internal fan creates negative pressure to suck in dust. When you use a pump to inflate a bicycle tire, you are creating positive pressure to force air into the tire.
Q: What is the most important factor to consider when choosing a pressure type?
A: The most critical factor is your specific application goal. Choose positive pressure when you need to push a substance or air out of a system (e.g., ventilation, spraying). Choose negative pressure when you need to draw a substance or air into a system (e.g., suction, extraction). Safety, precision, and environmental conditions are also important considerations.
Q: What are the calculation formulas for positive and negative pressure?
A: Both are based on comparison with atmospheric pressure (P<sub>atm</sub>).
Positive Pressure (Gauge): P<sub>gauge</sub> = P<sub>absolute</sub> - P<sub>atm</sub>
Negative Pressure (Vacuum): P<sub>vacuum</sub> = P<sub>atm</sub> - P<sub>absolute</sub>
Q: Why is understanding pressure types critical for selecting a sensor?
A: Clearly identifying whether you need to measure positive pressure, negative pressure, or both is the first step in selecting a sensor's range, type, and model. An incorrect choice can lead to inaccurate measurements, equipment damage, or even safety incidents. Understanding the nature of pressure in your application is fundamental to making the right selection.
HOT keyword: