Introduction
Pressure sensors and transmitters are crucial elements in diverse industrial applications for measuring and monitoring pressure. A pressure sensor is a device that measures the pressure of a fluid or gas and converts it into an electrical signal. On the other hand, a pressure transmitter takes the output from a pressure sensor and converts it into a standard signal that can be transmitted over a long distance and used by control systems.

Although they may seem similar at first glance, there are distinct differences between pressure sensors and pressure transmitters. Pressure sensors are typically designed to measure pressure at a specific location and provide a local indication or output. They may be used in applications where direct measurement of pressure is required, such as in industrial processes, automotive systems, or medical devices.
In contrast, pressure transmitters are more complex devices that are designed to transmit pressure information over a long distance. They often include additional features such as signal conditioning, amplification, and calibration to ensure accurate and reliable transmission of pressure data. Pressure transmitters are commonly used in applications where remote monitoring and control of pressure is required, such as in oil and gas pipelines, power plants, or water treatment facilities.
Pressure Sensors
Definition and Function
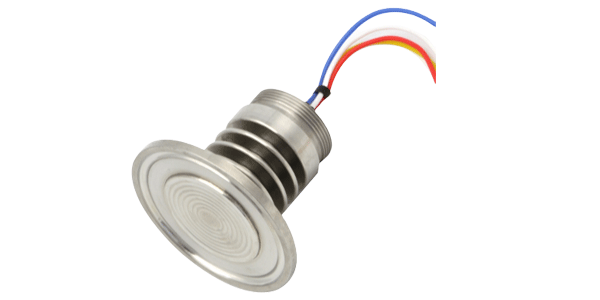
Pressure sensors are essential devices in various industrial and scientific fields as they measure and monitor pressure. They play a crucial role in providing accurate pressure readings for different applications.
Types of Pressure Sensors
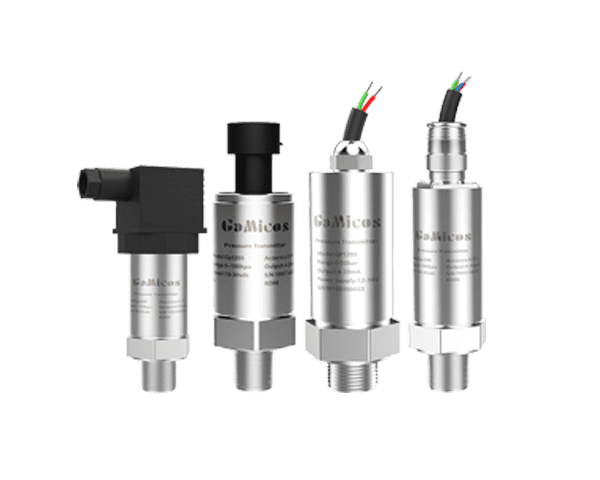
There are several types of pressure sensors available. For instance, DIF-PRESSURE SENSORS are widely used in intelligent industrial applications due to their imported high-quality sensors and great defending grade. They can work in caustic conditions and measure the temperature of high-temperature media when linked with external devices. Fiber optic pressure sensors offer unique advantages in certain applications. Micro Pressure Sensors are also popular for their specific characteristics. Additionally, there are many other types such as slurry line pressure sensors, piezoelectric pressure sensors, SAW pressure sensors, Nonelectric Pressure Sensors, Semiconductor pressure sensors, and hydraulic pressure sensors.
Working Principle
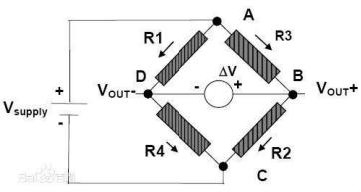
Pressure sensors deployed in monitoring regions form wireless sensor networks through self-organizing ways. They use elements like silicon and are often arranged in a way that allows for accurate measurement. For example, elements are placed in monitoring areas to detect pressure changes, and when the sensing element inside the pressure sensor is subjected to pressure, a Wheatstone bridge is formed, and the output will be millivolt signal. The output from these sensors can be used for various purposes depending on the application.
Pressure Transmitters
Definition and Function
A pressure transmitter is a device that converts the output signal of sensors into a recognizable signal for controllers or converts non-electrical signals into electrical signals for remote measurement and control. For example, pressure transmitters are often used in industrial applications where accurate and reliable transmission of pressure data is crucial. They play a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of processes such as oil and gas pipelines, power plants, and water treatment facilities.

Conversion Process
Pressure transmitters convert non-standard electrical signals into standard ones, such as 0-20mA or 4-20mA signals. This conversion process allows for seamless integration with control systems and enables remote monitoring and control. As seen in various applications, such as the design of a low power consumption wireless pressure transmitter or a leak detection and positioning system of an oil pipeline based on dynamic pressure transmitter, the conversion to standard signals is essential for accurate and efficient operation. Transmitters like these take the pressure information from sensors and transform it into a form that can be easily understood and utilized by different systems.
Differences between Pressure Sensors and Transmitters
Core Distinctions
The main differences between pressure sensors and transmitters lie in their functions of "transformation" and "transmission". Pressure sensors primarily convert non-electrical quantities, such as pressure, into electrical signals. They are responsible for detecting and transforming the physical pressure into an electrical output. For example, a pressure sensor might use a silicon element to sense pressure changes and generate an electrical signal proportional to the applied pressure.
On the other hand, pressure transmitters take the electrical signals from sensors and convert and amplify them for remote control. They not only perform the conversion but also ensure that the signal can be transmitted over long distances and used by control systems. Transmitters play a crucial role in industrial applications where remote monitoring and control are essential.
Signal Output
Pressure sensors may output non-standard signals with dimensional units. These signals are often specific to the type of sensor and its measurement range. For instance, a certain type of pressure sensor might output a signal in units of pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascals (kPa).
In contrast, pressure transmitters output standard signals without dimensional units. Commonly, they output signals such as 0-20mA or 4-20mA, which are easily recognizable and can be integrated into various control systems. These standard signals allow for seamless communication between different components of an industrial process and ensure accurate and reliable transmission of pressure data.
Conclusion
Summary of Differences
Pressure sensors primarily convert non-electrical quantities into electrical signals and are designed to measure pressure at a specific location. They output non-standard signals with dimensional units. In contrast, pressure transmitters take the electrical signals from sensors and convert and amplify them for remote control. They output standard signals without dimensional units and are crucial for remote monitoring and control in various industrial applications.
Importance in Industries
Both pressure sensors and transmitters play significant roles in different industries. In industrial process control, they help maintain accurate pressure levels for efficient operations. In flow measurement, they provide essential data for monitoring and regulating fluid flow. In medical instruments, pressure sensors and transmitters are used for measuring blood pressure, respiratory pressure, and other vital parameters. Additionally, in fields such as oil and gas pipelines, power plants, and water treatment facilities, pressure transmitters ensure the smooth operation by providing accurate and reliable pressure data for remote monitoring and control.